Preventing Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis B virus is usually spread when blood, semen, or another body fluid from a person infected with the Hepatitis B virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. The major, global routes of transmission are from mother to infant (perinatal), child to child (non-sexual person to person contact), sexual contact, and percutaneous exposure to blood or other infectious body fluids. Learn more about hepatitis B.
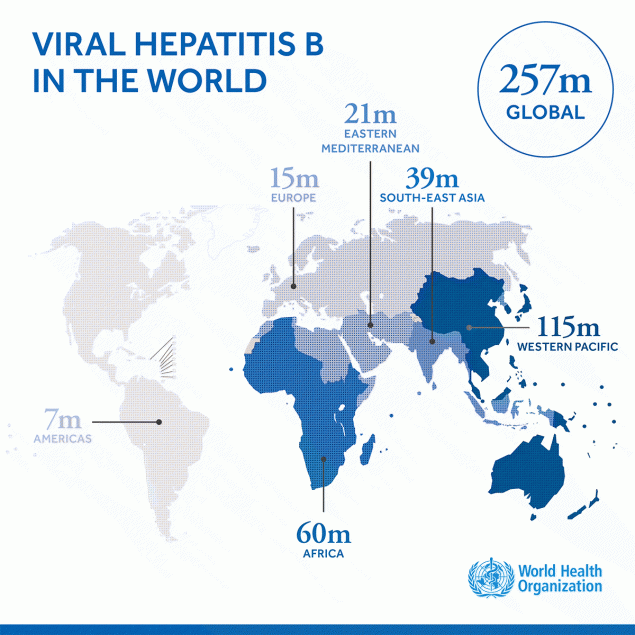
The best way to prevent Hepatitis B is by getting vaccinated. The World Health Organization recommends at least 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine for all infants with the first dose given within 24 hours of birth followed by 2 or 3 additional doses later. Globally, chronic Hepatitis B affects approximately 257 million people and contributes to an estimated 700,000 deaths worldwide every year.
CDC’s work to prevent hepatitis B
CDC provides both scientific and technical support to partners and countries in other parts of the world to decrease the burden of hepatitis B infection.
Documenting the magnitude of the problem
- Conduct surveys to evaluate the prevalence of hepatitis B among children in the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Haiti, Solomon Islands, and Tajikistan
- Conduct surveys to assess the burden of hepatitis B in pregnant women in Haiti to guide vaccination policy
- Assess the burden of hepatitis B in Afghanistan to determine if birth dose of hepatitis B vaccine should be introduced
- Assess the burden of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B in Africa to inform hepatitis B vaccine birth dose introduction
Diagnostics
- Assess whether or not hepatitis B can be detected through saliva (oral fluids)
- Assessing whether or not rapid field testing methods are accurate compared to the gold standard ELISA lab-based testing
Improving coverage of hepatitis B vaccine birth dose
- Pilot to evaluate best practices for using hepatitis B vaccine in a controlled temperature chain in rural Lao PDR, Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands; plan to scale up in 2017-2019
- Pilot to evaluate the impact of providing cell phones to village health volunteers to improve timely reporting of new home births and its impact on birth dose administration in Lao PDR
- Evaluating and improving birth dose implementation in health facilities in Cambodia, Lao PDR, the Philippines, and Papua New Guinea
- Evaluating selective hepatitis B birth dose vaccination in Sao Tome and Principe: a program assessment and cost-effectiveness study
- Contribute to the Global hepatitis B birth dose introduction guidelines
Evaluating the impact of hepatitis B vaccines after introduction
- Implement serosurveys in Bangladesh, Cambodia, the Philippines, South Pacific Islands (French Polynesia, Cook Islands, Tokelau, Tuvalu, Kiribati, Niue, Nauru), Papua New Guinea, and Oman to document the impact of hepatitis B vaccine and progress of countries to reach the hepatitis B control/elimination goal
- Implement a two-stage survey to verify the achievement of hepatitis B elimination in Colombia
- Assisting GAVI Alliance with estimating lives saved because of hepatitis B vaccine
Additional resources
- Recent Publications:
- The Status of Hepatitis B Control in the African Region
- Hepatitis B Vaccine Birth Dose Coverage Correlates Worldwide with Rates of Institutional Deliveries and Skilled Attendance at Birth
- Improving hepatitis B birth dose coverage through village health volunteer training and pregnant women education
- Evaluation of storing hepatitis B vaccine outside the cold chain in the Solomon Islands: identifying opportunities and barriers to implementation
- Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Pregnant Women in Haiti: a Cross-Sectional Serosurvey
- Improving hepatitis B birth dose in rural Lao People’s Democratic Republic through the use of mobile phones to facilitate communication
- Progress towards achieving hepatitis B control in the Cook Islands, Niue, Tokelau, and Kiribati
- Hepatitis B vaccine stored outside the cold chain setting: a pilot study in rural Lao PDR
- Hepatitis B Vaccination Coverage and Prevalence of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Among Children in French Polynesia, 2014
- Check out the World Hepatitis Alliance website for more resources and visit the World Health Organization for additional information on hepatitis B, including the Hepatitis B Fact Sheet.
- Page last reviewed: July 20, 2017
- Page last updated: July 20, 2017
- Content source:
Global Health
Notice: Linking to a non-federal site does not constitute an endorsement by HHS, CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the site.



 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir

