Have You Heard? 2016
HPV Vaccine
Monday, January 25, 2016
Boys and girls should get all three doses of HPV vaccine when they are 11 or 12 years old. But it’s not too late if a teen or young adult (through age 26) has not started or finished the series of three HPV vaccine shots Make an appointment today to get your child vaccinated. If you don’t have insurance, or your insurance does not cover vaccines, CDC’s Vaccines for Children program may be able to help.

Radon Exposure
Tuesday, January 19, 2016
Radon is a gas that you cannot smell, taste or see. Radon forms naturally when uranium, thorium, or radium–radioactive metals–breaks down in rocks, soil and groundwater. People can be exposed to radon primarily from breathing radon in air that comes through cracks and gaps in buildings and homes. Because radon comes naturally from the earth, people are always exposed to it. When you breathe in radon, radioactive particles from radon gas can get trapped in your lungs. Over time, these radioactive particles increase the risk of lung cancer. It may take years before health problems appear. • Having your home tested is the only effective way to determine whether you or your family is at risk of high radon exposure. • For more information on testing your home, check with your state radon office or call the National Radon Hotline at 1-800-SOS-RADON.
What Is Glaucoma?
Friday, January 15, 2016
Glaucoma is a group of diseases that can damage the eye’s optic nerve and result in vision loss and blindness. When glaucoma occurs, the normal fluid pressure inside the eyes slowly rises. Recent studies, however, show that people with normal eye pressure may also develop glaucoma. Fortunately, with early treatment of glaucoma, you can often protect your eyes against serious vision loss.

Teen Dating Violence
Monday, February 29, 2016
Unhealthy relationships can start early and last a lifetime. Teens might think some behaviors, like teasing and name calling, are a “normal” part of a relationship. However, in some cases, these behaviors can become abusive and develop into more serious forms of violence. Many teens do not report it because they are afraid to tell friends and family. What is teen dating violence? Teen dating violence is defined as the physical, sexual, psychological, or emotional violence within a dating relationship, including stalking. It can occur in person or electronically and might occur between a current or former dating partner. Several different words are used to describe teen dating violence. Below are just a few. • Relationship abuse • Intimate partner violence • Relationship violence • Dating abuse • Domestic abuse • Domestic violence

February is Heart Month
Monday, February 22, 2016
This American Heart Month, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Million Hearts®–a national initiative to prevent 1 million heart attacks and strokes in the United States by 2017– are challenging men to start one new, heart-healthy behavior. Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men, and African American men are disproportionately affected more by heart disease than other races or ethnicities. Uncontrolled high blood pressure is a leading cause of heart disease and stroke. In fact, about 75 million Americans have high blood pressure – and of that number, about half don’t have the condition under control. Research shows high blood pressure plays a role in nearly 7 out of 10 people having a first heart attack and nearly 8 out 10 people having a first stroke. High blood pressure often shows no signs or symptoms, which is why having your blood pressure checked regularly is important. It’s easy to get your blood pressure checked. You can get screened at your doctor’s office and drugstores or even check it yourself at home, using a home blood pressure monitor.

National Black HIV/AIDS Awareness
Monday, February 15, 2016
Compared with other racial/ethnic groups in the United States, blacks/African Americans have a disproportionate burden of HIV and AIDS. While blacks represent approximately 12% of the US population, they account for more new HIV diagnoses (44%) and people living with HIV (41%) than any other racial or ethnic group. Among all blacks, black gay and bisexual men account for the majority of new infections. Young black gay and bisexual men are especially affected. Nevertheless, we have seen encouraging signs of progress. From 2005 to 2014, new HIV diagnoses fell sharply (42%) among black women. Although new diagnoses among black gay and bisexual men rose significantly (22%) over the last decade, they have increased only slightly since 2010, suggesting that focused HIV prevention efforts are having an effect and need to continue.
Prostate Health
Tuesday, February 9, 2016
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system. Located above the bladder, the gland surrounds the urethra—the tube that empties the bladder of urine. If the prostate becomes enlarged, urinating can be difficult. After skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most common cancer affecting men in the U.S. The American Cancer Society estimates that approximately 200,000 new cases of prostate cancer are diagnosed each year, and approximately 30,000 men die of the disease. Because prostate cancer usually occurs in older men who are also at increased risk of heart disease and stroke, many men die with prostate cancer and not of the disease. Less than 10% of men die of prostate cancer within 5 years of diagnosis.
World TB Day 2016
Monday, March 28, 2016
Each year, we recognize World TB Day on March 24. This annual event commemorates the date in 1882 when Dr. Robert Koch announced his discovery of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacillus that causes tuberculosis (TB). Too many people in our country and around the world still suffer from TB. Anyone can get TB, and our current efforts to find and treat latent (undiscovered) TB infection and TB disease are not sufficient. Misdiagnosis of TB still exists and health care professionals often do not “think TB.” The theme of World TB Day 2016 is “End TB.” CDC and its partners, including the National TB Controllers Association, Stop TB USA, and the Stop TB Partnership are working together to eliminate this deadly disease. But we need your help.
What is Hemophilia?
Monday, March 21, 2016
Hemophilia is an inherited bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly. This can lead to spontaneous bleeding and bleeding after injuries or surgery. Hemophilia is caused by a mutation or change, in one of the genes that provides instructions for making the clotting factor proteins needed to form a blood clot. The best way to treat hemophilia is to replace the missing blood clotting factor so that the blood can clot properly. This is done by infusing (administering through a vein) commercially prepared factor concentrates. People with hemophilia can learn how to perform these infusions themselves so that they can stop bleeding episodes and, by performing the infusions on a regular basis, can even prevent most bleeding episodes.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease?
Monday, March 14, 2016
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a condition in which the kidneys are damaged and cannot filter blood as well as possible. The damage can cause wastes to build up in the body and lead to other health problems, including cardiovascular disease (CVD), anemia, and bone disease. People with early CKD tend not to have symptoms. The only ways to detect CKD are through a blood test to estimate kidney function and a urine test to assess kidney damage. CKD is usually irreversible and progressive and can lead to kidney failure over time if it is not treated. Once detected, CKD can be treated with medication and lifestyle changes to slow down the disease progression and prevent or delay the onset of kidney failure.
Facts about Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
Monday, March 7, 2016
HHT is a disorder in which some blood vessels do not develop properly. A person with HHT can form blood vessels without the capillaries (tiny blood vessels that pass blood from arteries to veins) usually present between arteries and veins. The space between an artery and a vein is often fragile and can burst and bleed much more easily than other blood vessels. Men, women, and children of all races and ethnicities can be affected by HHT and have health problems as a result. Some can be serious and potentially life-threatening. Although there is no cure for HHT, it can be effectively treated when discovered early.

National Infertility Awareness Week
Monday, April 25, 2016
In general, infertility is defined as not being able to get pregnant (conceive) after one year of unprotected sex. Women who do not have regular menstrual cycles, or are older than 35 years and have not conceived during a 6-month period of trying, should consider making an appointment with a reproductive endocrinologist—an infertility specialist. These doctors may also be able to help women with recurrent pregnancy loss—2 or more spontaneous miscarriages.

Infant Immunization Week
Monday, April 18, 2016
Infants are particularly vulnerable to infectious diseases; that is why it is critical to protect them with immunization. Each day, nearly 12,000 babies are born in the United States who will need to be immunized before age two against 14 serious diseases that can be prevented by vaccines. Immunizations help prevent the spread of disease and protect infants and toddlers against dangerous complications. Immunization is one of the most important things a parent can do to protect their children’s health. Failure to vaccinate can mean unnecessarily putting children at risk for serious diseases.

National Youth HIV & AIDS Awareness Day
Monday, April 11, 2016
HIV/AIDS is a serious threat to anyone of any age, but especially among youth. In the United States, an estimated 26% of all new HIV cases are in young people ages 13-24 years. Nearly 60% of these new infections in youth are in African Americans, about 20% in Hispanics/Latinos, and about 20% in whites. Despite this disproportionate number of new HIV infections among youth, the percentage of youth who get a test for HIV is low compared with other age groups. Only 1 in 5 sexually experienced U.S. high school students has ever been tested for HIV.

April Is Alcohol Awareness Month
Monday, April 4, 2016
Excessive alcohol use, including binge drinking, heavy drinking, and any alcohol use by people who are pregnant or under age 21, can lead to increased risk of health problems such as injuries, violence, liver diseases, and cancer.

What Is a Food Allergy?
Monday, May 30, 2016
A food allergy happens when the body has a specific and recurring immune response to certain foods. The immune response can be severe and life threatening, such as anaphylaxis. Although the immune system normally protects people, in people with food allergies, the immune system mistakenly responds to certain foods as if they were harmful. Eight foods or food groups account for 90% of serious allergic reactions in the United States: milk, eggs, fish, crustacean shellfish, wheat, soy, peanuts, and tree nuts.

Seat Belts Save Lives, Reduce Injuries
Monday, May 23, 2016
Motor vehicle crashes are a leading cause of death among people ages 1-54 in the United States. In 2012, more than 2.2 million adult drivers and passengers were treated in emergency departments as the result of being injured in motor vehicle crashes. In the same year, non-fatal crash injuries resulted in more than $50 billion in lifetime medical and work loss costs. Adult seat belt use is the most effective way to save lives and reduce injuries in crashes. Yet millions of adults don’t wear seat belts on every trip.

How Can You Tell If You Have Asthma?
Monday, May 16, 2016
It can be hard to tell if someone has asthma, especially in children younger than 5. Having a doctor check how well your lungs work and check for allergies can help you find out if you have asthma. During a checkup, the doctor will ask if you cough a lot, especially at night, and whether your breathing problems are worse after physical activity or at certain times of year. The doctor will also ask about chest tightness, wheezing, and colds lasting more than 10 days. The doctor will ask whether anyone in your family has or has had asthma, allergies, or other breathing problems, and ask questions about your home.

National Lightning Safety Awareness Week
Monday, June 27, 2016
Risks of lightning strikes – Although the odds of being struck by lightning in a given year are only around 1 in 500,000, some factors can put you at greater risk. Lightning most often strikes people who work outside or engage in outdoor recreational activities. Regional and seasonal differences can also affect your risk of being injured by lightning. – Safety precautions outdoors • If the weather forecast calls for thunderstorms, postpone your trip or activity. • Remember: When thunder roars, go indoors. Find a safe, enclosed shelter. • The main lightning safety guide is the 30-30 rule. After you see lightning, start counting to 30. If you hear thunder before you reach 30, go indoors. Suspend activities for at least 30 minutes after the last clap of thunder. • If no shelter is available, crouch low, with as little of your body touching the ground as possible. Lightning causes electric currents along the top of the ground that can be deadly from over 100 feet away. • Stay away from concrete floors or walls. Lightning can travel through any metal wires or bars in concrete walls or flooring. Although you should move into a non-concrete structure if possible, being indoors does not automatically protect you from lightning. In fact, about one-third of lightning-strike injuries happen indoors. – Safety precautions indoors • Avoid water during a thunderstorm. Lightning can travel through plumbing. • Avoid electronic equipment of all types. Lightning can travel through electrical systems and radio and television reception systems. Avoid corded phones. Cordless or cellular phones, however, are safe to use during a storm. • Avoid concrete floors and walls.

World Sickle Cell Day
Monday, June 20, 2016
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Healthy red blood cells are round, and they move through small blood vessels to carry oxygen to all parts of the body. In people who have SCD, the red blood cells become hard and sticky and look like a C-shaped farm tool called a “sickle.” The sickle cells die early, causing a constant shortage of red blood cells. Also, when they travel through small blood vessels, sickle cells get stuck and clog the blood flow. This can cause pain and other serious problems such as infection, acute chest syndrome, and stroke. People with SCD start to have signs of the disease during the first year of life, usually around 5 months of age. Symptoms and complications of SCD are different for each person and can range from mild to severe. There is no single best treatment for all people with SCD. Treatment options are different depending on the person’s symptoms. The only cure for SCD is bone marrow or stem cell transplant. Bone marrow is a soft, fatty tissue inside the center of the bones where blood cells are made. A bone marrow or stem cell transplant is a procedure that takes healthy cells that form blood from one person—the donor—and puts them into someone whose bone marrow is not working properly.

Men’s Health Week (June 13-19)
Monday, June 13, 2016
Take action to be healthy and safe and encourage men and boys in your life to make their health a priority. Learn about steps men can take each day to improve health. • Get Enough Sleep – Adults need 7 or more hours of sleep every day. Insufficient sleep is associated with a number of chronic diseases and conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, obesity, and depression. Also, poor sleep can result in motor vehicle and machinery-related accidents. • Move More – Adults need at least 2½ hours of moderate-intensity aerobic activity every week, and muscle-strengthening activities that work all major muscle groups (legs, hips, back, abdomen, chest, shoulders, and arms) on two or more days a week. You don’t have to do it all at once. Spread your activity out during the week, and break it into smaller amounts of time during the day. • Eat Healthy – Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables every day. Fruits and vegetables have many vitamins and minerals that may help protect you from chronic diseases. Limit foods and drinks high in calories, sugar, salt, fat, and alcohol. • Protect Your Skin – Men, especially those with lighter skin, are more likely than anybody else to get skin cancer, including melanoma—the deadliest kind of skin cancer. It’s easy to protect yourself from UV exposure with clothing, hats, sunscreen, and shade. Learn more about men and UV exposure • Prevent Cancer – Of cancers affecting both men and women, colorectal cancer (cancer of the colon and rectum) is the second leading cancer killer in the United States, but it doesn’t have to be. Screening can find precancerous polyps—abnormal growths in the colon or rectum—so they can be removed before turning into cancer. Screening also helps find colorectal cancer at an early stage, when treatment often leads to a cure. If you are 50 years old or older, get screened now. Learn more at Screen for Life.

Be a Healthy Swimmer
Monday, July 25, 2016
Swimming offers many health benefits, but it can also have health risks (for example, diarrhea, sunburn, and drowning). Swimmers and hot tub users should learn how to protect themselves and others from possible health problems. You can be a healthy swimmer by educating yourself and sharing information with family and friends.

You Can Prevent Stroke at Young Age
Monday, July 18, 2016
Stroke can happen at any age, yet many young people do not think a stroke could happen to them. Younger people may not recognize the symptoms, and there may be delay in diagnosis at the hospital because stroke is typically thought of as a condition that happens to older people. Knowing the signs of stroke can help younger people get the treatment they need in time to prevent long-term damage. Experts think younger people are having more strokes because more are obese and have high blood pressure and diabetes. Living a healthier lifestyle (more physical activity and good diet) can help prevent a stroke.

Group B Strep Awareness Month
Monday, July 11, 2016
Group B Streptococcus (group B strep or GBS) is a type of bacteria that causes illness in people of all ages. GBS disease can be especially severe in newborns, most commonly causing sepsis (infection of the blood), pneumonia (infection in the lungs), and sometimes meningitis (infection of the fluid and lining around the brain and spinal cord). The most common problems caused by GBS bacteria in adults are bloodstream infections, pneumonia, skin and soft-tissue infections, and bone and joint infections.

Keep Your Cool in Hot Weather
Monday, July 4, 2016
Now is the time to prepare for the high temperatures that can kill hundreds of people every year. Extreme heat caused 7,415 heat-related deaths in the United States from 1999 to 2010. Heat-related deaths and illness are preventable, yet every year many people die as a result of extreme heat. Take steps to stay cool, remain hydrated, and to keep informed. Getting too hot can make you sick. You can become ill from the heat if your body can’t compensate for it and properly cool you off.

Children’s Eye Health
Monday, August 22, 2016
In the United States, the most prevalent disabling childhood conditions are vision disorders including amblyopia, strabismus, and significant refractive errors. Early detection increases the likelihood of effective treatment; however, less than 15 percent of all preschool children receive an eye exam, and less than 22 percent of preschool children receive some type of vision screening.

National Immunization Awareness
Monday, August 15, 2016
National Immunization Awareness Month (NIAM) is an annual observance held in August to highlight the importance of vaccination for people of all ages. NIAM was established to encourage people of all ages to make sure they are up to date on the vaccines recommended for them. Communities have continued to use the month each year to raise awareness about the important role vaccines play in preventing serious, sometimes deadly, diseases.
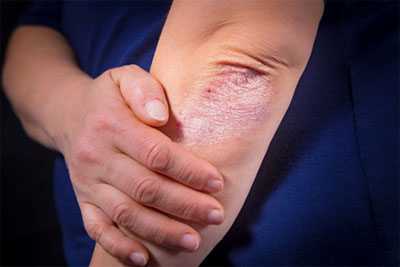
Psoriasis Awareness Month
Monday, August 8, 2016
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disease that speeds up the growth cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis causes patches of thick red skin and silvery scales. Patches are usually found on the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, face, palms, and soles of feet, but also can affect the fingernails, toenails,

National Breastfeeding Month
Monday, August 1, 2016
CDC’s Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity (DNPAO) is committed to increasing breastfeeding rates throughout the United States and to promoting and supporting optimal breastfeeding practices toward the ultimate goal of improving the public’s health. By following safe preparation and storage techniques, nursing mothers and caretakers of breastfed infants and children can maintain the high quality of expressed breast milk and the health of the baby.

Newborn Screening Awareness Month
Monday, September 26, 2016
Newborn screening identifies conditions that can affect a child’s long-term health or survival. Early detection, diagnosis, and intervention can prevent death or disability and enable children to reach their full potential. Each year, millions of babies in the U.S. are routinely screened, using a few drops of blood from the newborn’s heel, for certain genetic, endocrine, and metabolic disorders, and are also tested for hearing loss and critical congenital heart defects (CCHDs) prior to discharge from a hospital or birthing center.

Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Monday, September 19, 2016
Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin cancer among American men. Prostate cancers usually grow slowly. Most men with prostate cancer are older than 65 years and do not die from the disease. Finding and treating prostate cancer before symptoms occur may not improve your health or help you live longer. A prostate specific antigen (PSA) test may find prostate cancer at an earlier stage than if you don’t get screened, but most medical groups don’t recommend screening with the PSA test. Learn about prostate cancer and talk to your doctor before you decide to get tested or treated for prostate cancer.
Traumatic Brain Injury Awareness Month
Monday, September 12, 2016
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a serious public health problem in the United States. Each year, traumatic brain injuries contribute to a substantial number of deaths and cases of permanent disability. In 2010, 2.5 million TBIs occurred either as an isolated injury or along with other injuries. A TBI is caused by a bump, blow or jolt to the head or a penetrating head injury that disrupts the normal function of the brain. Not all blows or jolts to the head result in a TBI. The severity of a TBI may range from “mild,” i.e., a brief change in mental status or consciousness, to “severe,” i.e., an extended period of unconsciousness or amnesia after the injury.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation?
Monday, September 5, 2016
Atrial fibrillation, often called AFib or AF, is the most common type of heart arrhythmia. An arrhythmia is when the heart beats too slowly, too fast, or in an irregular way. When a person has AFib, the normal beating in the upper chambers of the heart (the two atria) is irregular, and blood doesn’t flow as well as it should from the atria to the lower chambers of the heart (the two ventricles). AFib may occur in brief episodes, or it may be a permanent condition.

Diabetes Awareness
Monday, October 31, 2016
Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned into glucose, or sugar, for our bodies to use for energy. The pancreas, an organ that lies near the stomach, makes a hormone called insulin to help glucose get into the cells of our bodies. When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use its own insulin as well as it should. This causes sugar to build up in your blood. Diabetes can cause serious health complications including heart disease, blindness, kidney failure, and lower-extremity amputations. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States.

Lung Cancer
Monday, November 14, 2016
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death and the second most common cancer among both men and women in the United States. The most important thing you can do to lower your lung cancer risk is to quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke. For help quitting, visit smokefree.gov, call 1 (800) QUIT-NOW (784-8669), or text “QUIT” to 47848 from your cell phone. The second leading cause of lung cancer is radon, a naturally occurring gas that comes from rocks and dirt and can get trapped in houses and buildings. Get your home tested for radon. People who have smoked for many years may want to think about screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT). Talk to your doctor about lung cancer screening and the possible benefits and harms. Lung cancer screening is not a substitute for quitting smoking.

Influenza
Tuesday, November 8, 2016
While current U.S. flu activity is low overall, CDC has received reports of localized influenza outbreaks, and activity is expected to increase in the coming weeks. CDC recommends a yearly flu vaccine for everyone 6 months and older. Now is a good time to get vaccinated. It takes about two weeks after vaccination for protection to set in. Flu vaccination can reduce flu illnesses and prevent flu-related hospitalizations. Flu vaccines have been updated for the 2016-2017 season. More than 120 million doses of seasonal influenza vaccine have been distributed at this time.

Handwashing Awareness Month
Monday, December 12, 2016
Fight Germs. Wash Your Hands! Handwashing gets rid of germs and chemicals that get on our hands every day. Known as the “do it yourself vaccine” the five simple steps (Wet, Lather, Scrub, Rinse, Dry) can reduce the spread of diarrheal and respiratory illness and keep you healthy! Regular handwashing, particularly before and after certain activities, is one of the best ways to remove germs, avoid getting sick, and prevent the spread of germs to others. It’s quick, it’s simple, and it can keep us all from getting sick. Handwashing is a win for everyone, except the germs. Keeping hands clean through improved hand hygiene is one of the most important steps we can take to avoid getting sick and spreading germs to others. Many diseases and conditions are spread by not washing hands with soap and clean, running water. CDC recommends cleaning hands in a specific way to avoid getting sick and spreading germs to others. The guidance for effective handwashing and use of hand sanitizer was developed based on data from a number of studies. If clean, running water is not accessible, as is common in many parts of the world, use soap and available water. If soap and water are unavailable, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol to clean hands.
National Influenza Vaccination Week
Tuesday, December 6, 2016
National Influenza Vaccination Week is December 4-10. The National Influenza Vaccination Week (NIVW) is a national awareness week focused on highlighting the importance of influenza vaccination. CDC recommends use of the flu shot (inactivated influenza vaccine or IIV) and the recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV). The nasal spray flu vaccine (live attenuated influenza vaccine or LAIV) should not be used during 2016-2017. Influenza (flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza. It can cause mild to severe illness. Serious outcomes of flu infection can result in hospitalization or death. Some people, such as older people, young children, and people with certain health conditions are at high risk for serious flu complications. The best way to prevent the flu is by getting vaccinated each year. Flu vaccination can reduce flu illnesses and prevent flu-related hospitalizations. While current U.S flu activity is low overall, localized influenza outbreaks have been reported and activity is expected to increase in the coming weeks. Click the ‘learn more’ link to see the latest Influenza Vaccination Recommendations.

World AIDS Day
Thursday, December 1, 2016
Each year World AIDS Day is observed on December 1. World AIDS Day is an opportunity for people to work actively and collaboratively with partners to unite all over the world to raise awareness in the fight against HIV. World AIDS Day began in 1988 to support people living with HIV and those who have died. An estimated 36.9 million people are living with HIV/AIDS worldwide. CDC provides support that helps more than 60 countries strengthen their national HIV/AIDS programs and build sustainable public health systems. CDC conducts these activities through the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) , the largest commitment by any nation to combat a single disease.
- Page last reviewed: January 15, 2016
- Page last updated: January 15, 2016
- Content source:



 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir