The Social-Ecological Model: A Framework for Prevention
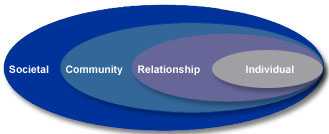 The ultimate goal is to stop violence before it begins. Prevention requires understanding the factors that influence violence. CDC uses a four-level social-ecological model to better understand violence and the effect of potential prevention strategies.¹ This model considers the complex interplay between individual, relationship, community, and societal factors. It allows us to understand the range of factors that put people at risk for violence or protect them from experiencing or perpetrating violence. The overlapping rings in the model illustrate how factors at one level influence factors at another level.
The ultimate goal is to stop violence before it begins. Prevention requires understanding the factors that influence violence. CDC uses a four-level social-ecological model to better understand violence and the effect of potential prevention strategies.¹ This model considers the complex interplay between individual, relationship, community, and societal factors. It allows us to understand the range of factors that put people at risk for violence or protect them from experiencing or perpetrating violence. The overlapping rings in the model illustrate how factors at one level influence factors at another level.
Besides helping to clarifying these factors, the model also suggests that in order to prevent violence, it is necessary to act across multiple levels of the model at the same time. This approach is more likely to sustain prevention efforts over time than any single intervention.
Individual
The first level identifies biological and personal history factors that increase the likelihood of becoming a victim or perpetrator of violence. Some of these factors are age, education, income, substance use, or history of abuse. Prevention strategies at this level are often designed to promote attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors that ultimately prevent violence. Specific approaches may include education and life skills training.
Relationship
The second level examines close relationships that may increase the risk of experiencing violence as a victim or perpetrator. A person’s closest social circle-peers, partners and family members-influences their behavior and contributes to their range of experience. Prevention strategies at this level may include parenting or family-focused prevention programs, and mentoring and peer programs designed to reduce conflict, foster problem solving skills, and promote healthy relationships.
Community
The third level explores the settings, such as schools, workplaces, and neighborhoods, in which social relationships occur and seeks to identify the characteristics of these settings that are associated with becoming victims or perpetrators of violence. Prevention strategies at this level are typically designed to impact the social and physical environment – for example, by reducing social isolation, improving economic and housing opportunities in neighborhoods, as well as the climate, processes, and policies within school and workplace settings.
Societal
The fourth level looks at the broad societal factors that help create a climate in which violence is encouraged or inhibited. These factors include social and cultural norms that support violence as an acceptable way to resolve conflicts. Other large societal factors include the health, economic, educational and social policies that help to maintain economic or social inequalities between groups in society.
Reference
1. Dahlberg LL, Krug EG. Violence-a global public health problem. In: Krug E, Dahlberg LL, Mercy JA, Zwi AB, Lozano R, eds. World Report on Violence and Health. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2002:1–56.
- Page last reviewed: March 25, 2015
- Page last updated: March 25, 2015
- Content Source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir
