We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Acromioclavicular injuries
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Occurs via direct trauma to the adducted shoulder
- Acromioclavicular and coracoclavicular ligaments may be affected
- Routine use of stress radiographs is controversial (low yield)
Clinical Features
- Tenderness directly over AC joint (with possible deformity)
- AC compression test
- Passively flex arm so It is parallel with ground; then passively adduct across body
- Pain suggests AC joint injury
- Passively flex arm so It is parallel with ground; then passively adduct across body
Differential Diagnosis
Shoulder and Upper Arm Diagnoses
Traumatic/Acute:
- Shoulder Dislocation
- Clavicle fracture
- Humerus fracture
- Scapula fracture
- Acromioclavicular injury
- Glenohumeral instability
- Rotator cuff tear
- Biceps tendon rupture
- Triceps tendon rupture
- Septic joint
Nontraumatic/Chronic:
- Rotator cuff tear
- Impingement syndrome
- Calcific tendinitis
- Adhesive capsulitis
- Biceps tendinitis
- Subacromial bursitis
Refered pain & non-orthopedic causes:
- Referred pain from
- Neck
- Diaphragm (e.g. gallbladder disease)
- Brachial plexus injury
- Axillary artery thrombosis
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Subclavian steal syndrome
- Pancoast tumor
- Myocardial infarction
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism
Evaluation
Imaging
- AP shoulder (highly consider comparison view)
- AC joint
- Normal width of AC joint in adults is 1-3mm
- By age 60 width is often less than 1mm
- Children and adolescents have a slightly wider joint space
- CC joint
- Normal distance is 11-13mm
- Comparison to opposite CC joint space is more important
- Increase in CC distance of 25-50% indicates complete CC ligament disruption
- Zanca view (AP with 10-15 degree cephalic tilt)
- Consider if AP view is ambiguous, concern for type II injury or distal clavicle injury
- Axillary view
- Obtain if coracoid tenderness is present to rule-out associated coracoid fracture
- Helps to confirm ant-post position of clavicle in injury types III-IV
- AC joint
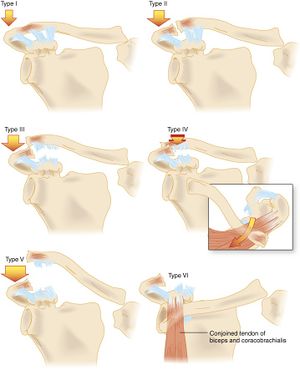
Classification
Type 1
- AC ligament sprain; AC joint intact
- Exam
- Mild swelling, no deformity
- CC ligaments are nontender
- Only distal-most 1-2cm of clavicle is tender
- Active overhead and cross-body ROM are limited by pain
- X-ray
- Often no abnormality is seen on xray; slight widening of the AC joint may occur
Type 2
- AC ligament torn; coracoclavicular (CC) ligament may be partially torn but is intact
- Exam
- Prominent and tender AC joint with significant swelling
- Minimal tenderness of CC ligaments reflecting lack of significant injury
- May be instability of the distal clavicle in the horizontal plane
- X-ray
- Partial elevation of the distal clavicle with no or minimal widening of CC distance
Type 3
- AC and CC ligaments torn; complete dislocation of the joint
- Exam
- Deformity of the AC joint is clearly visible
- Marked tenderness of CC ligaments (helps distinguish Type 3 from type 2)
- X-ray
- Elevated distal clavicle and increased CC distance
- Distal clavicle is positioned above the plane of the top of the acromion
Type 4
- Complete dislocation with posterior displacement of distal clavicle in/through trapezius
- Exam
- Palpable posterior fullness or deformity despite significant swelling
- SC dislocation may be appreciated
- X-ray
- Axillary view required to visualize the posterior dislocation
Type 5
- More severe form of type III injury
- Superior dislocation of the joint of 1-3x the normal spacing
- CC ligament distance is increased 2-3x normal
- Disruption of the deltotrapezial fascia
- Exam
- Shoulder appears to droop
- Severe superior displacement of clavicle (may cause tenting, ischemia of skin)
- Clavicle is perhced above the muscle and does not reduce when patient shrugs shoulder
- X-ray
- Clavicle is elevated above acromion approximately 1-3x width of the clavicle
- CC distance is increased 2-3x normal range
Type 6
- Complete dislocation with clavicle displaced inferiorly
- X-ray
- Complete disruption of the AC and CC ligaments
Management
Type 1
- Rest, ice, sling
- ROM and strengthening exercises as soon as tolerated
- Return to sport or work is limited only by pain
Type 2
- Rest, ice, sling x3-7 days
- ROM and strenghtnening exercises as soon as tolerated
- Return to sport or work once full ROM and strength are regained
Type 3
- Rest, ice, sling x2-3 weeks
- ROM and strengthening exercises as soon as tolerated
- Return to sport or work 6-12 weeks following injury
- Ortho consultation within 1 week
Types 4-6
- Require orthopedic evaluation; emergent if neurovascular compromise exists
- Generally operative
See Also
References
Authors
Ross Donaldson, Jordan Swartz, Neil Young, Tianjiang Ye, Daniel Ostermayer, Claire