We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Corneal ulcer
From WikEM
(Redirected from Corneal ulcers)
Contents
Background
- Major cause of impaired vision and blindness worldwide
- Break in epithelial layer allows infectious agents to gain access to the underlying stroma
- Risk factors include: incomplete lid closure (e.g. secondary to Bell’s palsy) and soft contact lenses use (especially sleeping in contacts)
Causes
Clinical Features
- Redness and swelling of lids and conjunctiva
- Ocular pain or foreign body sensation
- Decreased visual acuity (if located in central visual axis or uveal tract is inflamed)
- Photophobia
Differential Diagnosis
Unilateral Red Eye
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma^
- Anterior uveitis
- Caustic keratoconjunctivitis^^
- Conjunctival laceration
- Conjunctivitis
- Corneal abrasion
- Corneal erosion
- Ocular foreign body
- Corneal ulcer^
- Endophthalmitis^
- Episcleritis
- Globe rupture^
- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
- Intraocular foreign body
- Inflamed pingueculum
- Inflamed Pterygium
- Keratoconjunctivitis
- Keratoconus
- Lens dislocation
- Nontraumatic iritis
- Scleritis^
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage
- Traumatic hyphema
- Traumatic iritis
- Ultraviolet keratitis
^Emergent diagnoses
^^Critical diagnoses
Evaluation
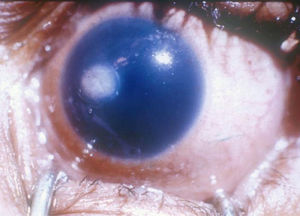
- Slit-lamp exam
- Gray/white lesion
- Hypopyon may be present
- Iritis signs may be present:
- Miotic pupil
- Consenual photophobia
Management
- Emergent ophtho consultation
- Topical antibiotics
- Ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin otic, 1 drop qhr in affected eye
- Antiviral or anti-fungal if high suspicion for viral or fungal cause
- Cycloplegic
- Helps with pain from accompanying iritis
- Cyclopentolate 1%
- Do not patch the eye
Disposition
Refer to ophtho within 12-24hr
Complications
- Corneal scarring
- Corneal perforation
- Ant/posterior synechiae
- Glaucoma
- Cataracts