We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
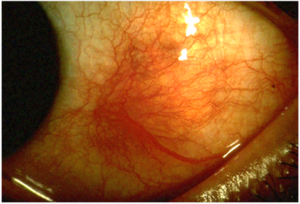
Scleritis
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Potentially blinding disorder
- Sclera fuses with dura mater and arachnoid sheath of the opic nerve
- Reason why optic nerve edema and visual compromise are common complications
- 50% of cases associated with an underlying disorder:
Clinical Features
- Essential sign is scleral edema, usually accompanied by violaceous discoloration of the globe
- Intense ocular pain that radiates to the face
- Pain with EOM (extraocular muscles insert into the sclera)
- Photophobia
- Globe tenderness to palpation
- Episcleral vessel dilation
DifferentialDiagnosis
Unilateral Red Eye
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma^
- Anterior uveitis
- Caustic keratoconjunctivitis^^
- Conjunctival laceration
- Conjunctivitis
- Corneal abrasion
- Corneal erosion
- Ocular foreign body
- Corneal ulcer^
- Endophthalmitis^
- Episcleritis
- Globe rupture^
- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
- Intraocular foreign body
- Inflamed pingueculum
- Inflamed Pterygium
- Keratoconjunctivitis
- Keratoconus
- Lens dislocation
- Nontraumatic iritis
- Scleritis^
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage
- Traumatic hyphema
- Traumatic iritis
- Ultraviolet keratitis
^Emergent diagnoses
^^Critical diagnoses
Evaluation
- Labs (to assess possible associated disease)
- CBC
- Chemistry
- Urinalysis
- Rule-out glomerulonephritis
- ESR, CRP
- Posterior Scleritis (posterior to the insertion of the extraocular muscles)
- Physical exam often benign
- Inflammation may sometimes be seen at the extremes of gaze
- Patient complains of pain, pain upon EOM
- Involvement of the optic nerve and retina is common
- Retinal detachment, optic disc edema
- Physical exam often benign
Imaging
- Ultrasound and CT can show thickening of the sclera
Management
- Systemic therapy with NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, or other immunosuppressive drugs
- NSAIDs
- Indomethacin 25-75mg PO TID
Disposition
- Urgent ophtho consult
Complications
- Cornea
- Peripheral ulcerative keratitis > irreversible loss of vision
- Uveal tract
- Anterior uveitis seen in 40%
- Spillover of inflammation from the sclera
- Anterior uveitis seen in 40%
- Posterior segment
- Retinal detachment, optic disc edema
See Also
References
Authors
Ross Donaldson, Jordan Swartz, Claire, Neil Young, Daniel Ostermayer