We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Scurvy
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Nutritional deficiency of Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid)
- Vitamin C is typically foundin fruits and vegetables.
- Vitamin C is a cofactor for hydroxylation of proline and lysine amino acids in procollagen molecules, which is required for cross-linking collagen's triple helix.
- Scurvy therefore leads to unstable collagen and collagen fragility.
- leaking of vascular structures
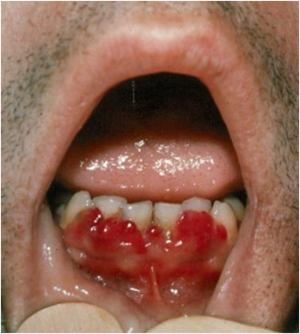
- gingival bleeding
- petechiae
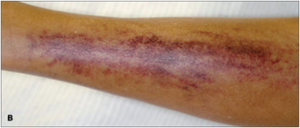
- easy bruising
- leaking of vascular structures
- Vitamin C is also required for the disulfide bonding in hair leading to corkscrew appearance of hair.
Clinical Features
- Gingival bleeding
- Easy bruising
- Petechiae
- Corkscrew hair
Differential Diagnosis
Petechiae/Purpura (by cause)
- Abnormal platelet count and/or coagulation
- Septicemia
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome
- Leukemia
- Coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia)
- Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP)
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI)
- Hypersensitivity vasculitis
- Primary vasculitides
- Wegener's
- Microscopic polyangiitis
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome)
- Secondary vasculitides
- Connective tissue disorder
- Scurvy
- Infectious disease
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Trauma
Dentoalveolar Injuries
Odontogenic Infections
- Dental caries (pulpitis)
- Ludwig's angina
- Periapical abcess
- Periodontal abscess
- Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA)
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Trench Mouth (Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis)
- Vincent's angina - tonsillitis and pharyngitis
- Acute alveolar osteitis
Other
- Scurvy
- Gingival hyperplasia
- Phenytoin
- Cyclosporine
- Nifedipine, Amlodipine
- Leukemia
Vitamin deficiencies
- Vitamin A deficiency
- Vitamin B deficiencies
- Vitamin B1 deficiency (Thiamine)
- Vitamin B3 deficiency (Pellagra)
- Vitamin B9 deficiency (Folate)
- Vitamin B7 deficiency (Biotin)
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Vitamin C deficiency (Scurvy)
- Vitamin D deficiency (Rickets)
- Vitamin E deficiency
- Vitamin K deficiency
Evaluation
- Guided by clinical suspicion but confirmed with laboratory analysis of vitamin C levels.
Management
- Vitamin C supplementation.
Disposition
See Also
External Links
References
- Kluesner, Nicholas and Miller, daniel. “Scurvy: Malnourishment in the land of the plenty.” The journal of emergency medicine. Vol 46. no 4. pages 530-532. 2014.
- Maltos, andre, et al. “Scurvy in a patient with AIDS: case report.” Revista de sociedade brasileira de medicina tropical 44(1): 122-123. 2011.