We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Streptococcal pharyngitis
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Peak in 5-15yr old
- Rare in <2yr of age
- Accounts for only 15-30% of pharyngitis
Clinical Features
- Sore throat
- Painful swallowing
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
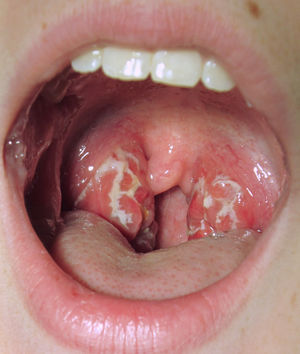
- Tonsillar exudate
- Palatal petechiae
Differential Diagnosis
Acute Sore Throat
Bacterial infections
- Streptococcal pharyngitis (Strep Throat)
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Diphtheria (C. diptheriae)
- Bacterial Tracheitis
Viral infections
- Infectious mononucleosis (EBV)
- Patients with peritonsillar abscess have a 20% incidence of mononucleosis [1]
- Laryngitis
- Acute Bronchitis
- Rhinovirus
- Coronavirus
- Adenovirus
- Herpesvirus
- Influenza virus
- Coxsackievirus
- HIV (Acute Retroviral Syndrome)
Noninfectious
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- Pemphigus
- Angioedema
Other
- Deep neck space infection
- Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA)
- Epiglottitis
- Kawasaki disease
- Penetrating injury
- Caustic ingestion
- Lemierre's syndrome
- Peritonsillar cellulitis
- Lymphoma
- Internal carotid artery aneurysm
- Oral Thrush
- Parotitis
- Post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage
Oral rashes and lesions
- Angioedema
- Aphthous stomatitis
- Herpes gingivostomatitis
- Herpes labialis
- Measles (Koplik's spots)
- Perioral dermatitis
- Oral thrush
- Steven Johnson syndrome
- Strep pharyngitis
Evaluation
Modified Centor Criteria[2]
One point is given for each of the criteria:[2]
- Absence of a cough
- Swollen and tender cervical lymph nodes
- Temperature >38.0 °C (100.4 °F)
- Tonsillar exudate or swelling
- Age less than 15^
- Subtract a point if age >44
^Testing is not needed in children <3 years old as both group A strep and rheumatic fever are rare, except if they have a sibling with the disease.[3]
| Points | Probability of Streptococcal pharyngitis | Management |
|---|---|---|
| 1 or fewer | <10% | No antibiotic or culture needed |
| 2 | 11–17% | Antibiotic based on rapid strep or culture |
| 3 | 28–35% | |
| 4 or 5 | 52% | Empiric antibiotics |
Management
Antibiotics
Treatment can be delayed for up to 9 days and still prevent major sequelae
Penicillin Options:[4]
- Penicillin V 250mg PO BID x 10d (child) or 500mg BID x 10d (adolescent)
- Bicillin L-A 25-50K mg/kg IM x 1 (max dose = 1.2million)
Penicillin allergic (mild):[4]
- Cefuroxime 10mg/kg PO QID x 10d (child) or 250mg PO BID x 4d
Penicillin allergic (anaphylaxis):[4]
- Clindamycin 7.5mg/kg PO QID x 10d (child) or 450mg PO TID x 10d OR
- Azithromycin 12mg/kg QD (child) or 500mg on day 1; then 250mg on days 2-5
Steroids
- Single dose of dexamethasone shortens duration of pain[5]
- Dexamethasone 0.6mg/kg PO - maximum of 10mg
Disposition
- Discharge
Complications
- Acute rheumatic fever
- Scarlet fever
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Post-streptococcal glomerular nephritis
- PANDAS syndrome
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Cervical lymphadenitis
- Mastoiditis
See Also
References
- ↑ Melio, Frantz, and Laurel Berge. “Upper Respiratory Tract Infection.” In Rosen’s Emergency Medicine., 8th ed. Vol. 1, n.d.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Choby BA (March 2009). "Diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis". Am Fam Physician 79 (5): 383–90. PMID 19275067.
- ↑ Shulman, ST; Bisno, AL; Clegg, HW; Gerber, MA; Kaplan, EL; Lee, G; Martin, JM; Van Beneden, C (Sep 9, 2012). "Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America.". Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America 55 (10): e86–102. doi:10.1093/cid/cis629. PMID 22965026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 ID society guidelines
- ↑ Hayward G, Thompson MJ, Perera R, Glasziou PP, Del Mar CB, Heneghan CJ. Corticosteroids as standalone or add-on treatment for sore throat. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10:CD008268. PMID: 23076943.