The Young Men Who Have Sex With Men (YMSM) Project
Reducing the Risk of HIV/STD Infection
The goal of the YMSM Project is to reduce the risk of HIV and STD infection in YMSM students (ages 13–19) with a focus on black and Latino YMSM. To accomplish this goal, the project works to:
- Increase the number of teen YMSM who are tested and treated for HIV and STD
- Decrease sexual risk behaviors among teen YMSM
- Reduce absenteeism and school drop-out among teen YMSM
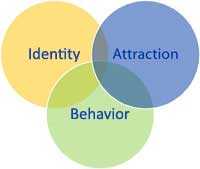
For this project, “YMSM” includes young men who identify as gay or bisexual, are attracted to other males, and/or engage in sexual behavior with other males.
The YMSM Project’s innovative, school-centered approach is led by CDC’s Division of Adolescent and School Health (DASH). The project is funded jointly by the Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention (DHAP) and DASH through the cooperative agreement RFA-1308: Promoting Adolescent Health Through School-Based HIV/STD Prevention and School-Based Surveillance [PDF – 771K] .
Four partners are funded to address the HIV/STD Prevention needs of black and Latino YMSM:
- Advocates for Youth
- Los Angeles Unified School District (California)
- San Francisco Unified School District (California)
- School Board of Broward County (Florida)
The project is guided by the National HIV/AIDS Strategy. Funded partners implement multiple activities to meet the local HIV/STD prevention needs of black and Latino YMSM in priority schools:
- Implement or expand HIV and STD testing and treatment in schools and school-based health centers
- Increase collaboration between schools, school-based health centers, community-based organizations, and other health care providers for linkage and referral to HIV and STD testing and treatment, and evidence-based educational interventions
- Develop a systematic process for school staff (e.g., nurses, counselors, and social workers) to refer students to HIV and STD testing and treatment
- Assess and implement policies that impact HIV and STD-related testing, treatment, and prevention interventions for teen YMSM
- Implement programs to promote healthy school and school-based health center environments for YMSM
- Market HIV/STD prevention to teen YMSM
- Implement evidence-based HIV prevention interventions tailored for teen YMSM
HIV/STD Among YMSM: Facts at a Glance
- Among adolescent males aged 13–19 years in 2011, 93% of diagnosed HIV infections were attributed to male-to-male sexual contact.1
- From 2008 to 2011, the estimated number of new HIV infections increased 26% among YMSM aged 13–24 years.2
- In 2011, among all YMSM aged 13–24 years with HIV infection, an estimated 58% were black, 20% were Hispanic/Latino, and 18% were white.2
- About 60% of all youth with HIV do not know they are infected, are not getting treated, and can unknowingly pass the virus on to others.3
References
- CDC. HIV Surveillance in Adolescents and Young Adults (through 2011). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC Web site. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_surveillance_Adolescents.pdf [PDF – 4.7MB].
- CDC. HIV Surveillance in Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM)(through 2011). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC Web site. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_surveillance_MSM.pdf.
- CDC. Vital Signs: HIV Infection, Testing, and Risk Behaviors Among Youths — United States. MMWR 2012:61(47);971-976.
Related Resources
- Page last reviewed: September 1, 2015
- Page last updated: September 1, 2015
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir