We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
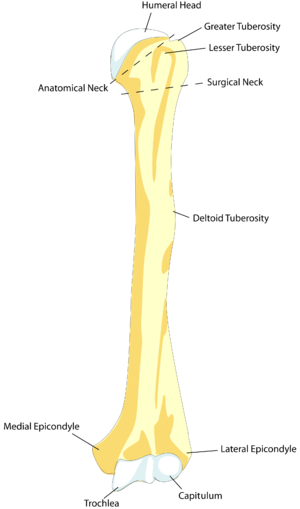
Humerus shaft fracture
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Peaks in third and seventh decades of life (young men and osteoporotic elderly women)
- Occurs via direct blow or FOOSH
- Common site of pathologic fractures (esp breast cancer)
- Rule-out radial nerve injury (wrist drop - no ext of wrist, fingers, or thumb)
Clinical Features
- Localized tenderness, swelling, pain
Differential Diagnosis
Humerus Fractures
Shoulder and Upper Arm Diagnoses
Traumatic/Acute:
- Shoulder Dislocation
- Clavicle fracture
- Humerus fracture
- Scapula fracture
- Acromioclavicular injury
- Glenohumeral instability
- Rotator cuff tear
- Biceps tendon rupture
- Triceps tendon rupture
- Septic joint
Nontraumatic/Chronic:
- Rotator cuff tear
- Impingement syndrome
- Calcific tendinitis
- Adhesive capsulitis
- Biceps tendinitis
- Subacromial bursitis
Refered pain & non-orthopedic causes:
- Referred pain from
- Neck
- Diaphragm (e.g. gallbladder disease)
- Brachial plexus injury
- Axillary artery thrombosis
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Subclavian steal syndrome
- Pancoast tumor
- Myocardial infarction
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism
Evaluation
- Obtain views of humerus, elbow and shoulder
Management
Non Operative
- Most do not need surgery if
- Less than 20% anterior angulation
- 30% varus/valgus angulation
- < 3cm shortening
Operative
- Neurovascular injury
- Significant soft tissue injury
- Open fracture
- Concern for compartment syndrome
- Floating elbow (ipsilateral forearm fracture)
- Neurovascular injury (radial nerve injury not contraindication to splinting)
Treatment in the ED for either
- Option 1: Long Arm Posterior Splint
- Option 2:
- Stable: coaptation splint (upper arm sugar-tong splint)
- Unstable: elephant ear
References
- Orthobullets
Disposition
- Outpatient ortho referral (if adequate pain control)
See Also
References
Authors
Ross Donaldson, Jonathan Snyder, Neil Young, Daniel Ostermayer