We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Vertigo
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Perception of movement (rotational or otherwise) where no movement exists
- Pathophysiology
- Mismatch or asymmetric activity of visual, vestibular, and/or proprioceptive systems
- Must distinguish peripheral from central cause
- Peripheral: 8th CN, vestibular apparatus
- Central: Brainstem, cerebellum
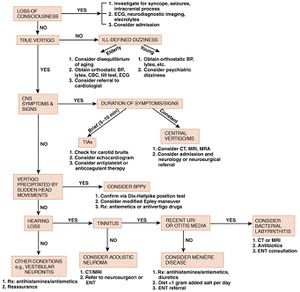
Clinical Features
Classification[1]
- Triggered Vestibular Syndrome
- Triggered by movement (change in body position, head mvmt, valsalva)
- Lasts sec to hours w/ asymptomatic periods in between
- Benign:BPPV (Dix Hallpike), Orthostatic Hypotension (fluids)
- Dangerous: Posterior Fossa Tumor
- Episodic Vestibular Syndrome
- Acute Vestibular Syndrome (AVS)
- Abrupt and persistent
- Can be exacerbated by movement but not triggered by it
- Benign: Vestibular Neuritis, Labyrinthitis,
- Dangerous: Posterior Stroke
- Utilize HINTS Exam to differentiate
- Remember, the HINTS Exam can only be used on symptomatic AVS patients according to the study[2]
Central vs. Peripheral Causes of Vertigo
| Peripheral | Central | |
| Onset | Sudden | Sudden or slow |
| Severity | Intense spinning | Ill defined, less intense |
| Pattern | Paroxysmal, intermittent | Constant |
| Aggravated by position/movement | Yes | Variable |
| Nausea/diaphoresis | Frequent | Variable |
| Nystagmus | Horizontal and unidirectional | Vertical and/or multidirectional |
| Fatigue of symptoms/signs | Yes | No |
| Hearing loss/tinnitus | May occur | Does not occur |
| Abnormal tympanic membrane | May occur | Does not occur |
| CNS symptoms/signs | Absent | Usually present |
Differential Diagnosis
Vertigo
- Vestibular/otologic
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
- Traumatic (following head injury)
- Infection
- Meniere's disease
- Ear foreign body
- Otic barotrauma
- Neurologic
- Cerebellar stroke
- Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
- Lateral Wallenberg syndrome
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome
- Neoplastic: cerebellopontine angle tumors
- Basal ganglion diseases
- Vertebral Artery Disssection
- Multiple sclerosis
- Infections: neurosyphilis, tuberculosis
- Epilepsy
- Migraine (basilar)
- Other
- Hematologic: anemia, polycythemia, hyperviscosity syndrome
- Toxic
- Chronic renal failure
- Metabolic
Evaluation
Work-up
- Glucose check
- Full neuro exam
- TM exam
- CTA or MRA (diagnostic study of choice) of the neck/brain if symptoms consistent with central cause
| Test | Sensitivity |
| HINTS | 100% |
| MRI (24hrs) | 68.40%[3] |
| MRI (48hrs) | 81%[3] |
| CT non con | 26%[4] |
HINTS Exam
Proposed as method of distinguishing peripheral cause from cerebellar/brain stem CVA in the Emergency Department population [5][6][7]
The 3 components of the HINTS exam include:
- Head impulse test of vestibulo-ocular reflex function
- Observation for nystagmus in primary, right, and left gaze
- Alternate cover test for skew deviation.
Head Impulse Test:
- Normally, a functional vestibular system will identify any movement of the head position and rapidly correct eye movement accordingly so that the center of the vision remains on a target. This reflex fails in peripheral causes of vertigo effective the vestibulocochlear nerve
- Have patient fix their eyes on your nose
- Move their head in the horizontal plane to the left and righ
- When the head is turned towards the normal side the vestibular ocular reflex remains intact and eyes continue to fixate on the visual target
- When the head is turned towards the affected side, the vestibular ocular reflex fails and the eyes make a corrective saccade to re-fixate on the visual target [8][9]
- It is reassuring if the reflex is abnormal (due to dysfunction of the peripheral nerve)
Test of Skew
- Skew deviation is a fairly specific predictor of brainstem involvement in patients with acute vestibular syndrome. The presence of skew may help identify stroke when a positive head impulse test falsely suggests a peripheral lesion.
- Skew is also known vertical dysconjugate gaze and is a sign of a central lesion
- Have pt look at your nose with their eyes and then cover one eye
- Then rapidly uncover the eye and quickly look to see if the eye moves to re-align.
- Repeat with on each eye
- A positive HINTS exam: 100% sensitive and 96% specific for the presence of a central lesion.
- The HINTS exam was more sensitive than general neurological signs: 100% versus 51%.
- The sensitivity of early MRI with DWI for lateral medullary or pontine stroke was lower than that of the HINTS examination (72% versus 100%, P=0.004) with comparable specificity (100% versus 96%, P=1.0).
- If any of the above 3 tests are consistent with CVA obtain full work-up (including MRI)
Management
Peripheral
Symptomatic control
- Antihistamines: inhibit vestibular stimulation and vestibular-cerebellar pathways
- Meclizine (Antivert) 25mg PO QID
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) 25-50mg IM, IV, or PO q4hr
- Anticholinergics
- Scopolamine transdermal patch 0.5mg (behind ear) QID
- Antidopaminergics
- Metoclopramide 10-20 IV or PO TID
Cause Reversal
- Epley maneuver (see BPPV)
Central
- Rule out CVA
- MRI
- Rule out vascular insufficiency
Disposition
- Most patients with peripheral vertigo can be discharged home
- All patients with central vertigo require urgent imaging and consultation while in the ED
See Also
References
- ↑ Edlow JA, Newman-Toker D. Using the Physical Exam to Diagnose Patients with Acute Dizziness and Vertigo. J Emerg Med. 2016 Apr 50(4): 617-28.
- ↑ Kattah, J. et al. "HINTS to Diagnose Stroke in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome: Three-Step Bedside Oculomotor Examination More Sensitive Than Early MRI Diffusion-Weighted Imaging". Stroke. 2009. 40(11):3504–3510.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 ../docss/CNS-EBN_cat-document_2010-07-JUL-30_a-negative-dwi-mri-within-48-hours-of-stroke-symptoms-ruled-out-anterior-circulation-stroke_4494E.pdf
- ↑ Chalela JA, Kidwell CS, Nentwich LM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in emergency assessment of patients with suspected acute stroke: a prospective comparison. Lancet. 2007;369:293–8.
- ↑ ../docss/hints-exam.pdf?d13a76d516d9dec20c3d276ce028ed5089ab1ce3dae902ea1d01c0873ed8cc5fe910&c_id=2502227
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18541870
- ↑ ../docss/diff-of-vertigo.pdf?c_id=2502226&expiration=1380995436&hwt=0a8bc67ea910e018a1543ebea192f668
- ↑ Barraclough K, Bronstein A. Vertigo. BMJ. 2009;339:b3493
- ↑ Kuo CH, Pang L, Chang R. Vertigo - part 1 - assessment in general practice. Aust Fam Physician. 2008;37(5):341-7