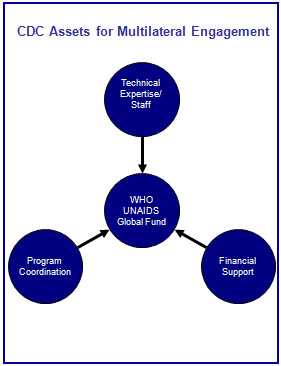
Collaborations with International Organizations
Through the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), CDC supports a comprehensive and amplified response to global HIV/AIDS through leadership of, engagement in, and coordination with multilateral institutions and international organizations—including the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations Joint Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (Global Fund)—in the areas of prevention, treatment, use of strategic information to support program planning and implementation, capacity building at the national and district level, and laboratory systems development.
CDC-UNAIDS Collaboration
CDC provides technical expertise and financial support to guide efforts against HIV worldwide, as well as tracking, monitoring, and evaluation of the epidemic. CDC works with UNAIDS to develop guidelines on key health information systems policy and implementation issues such as data confidentiality and security, and on methodology for combining data originating in different clinical and monitoring systems.
CDC strengthens UNAIDS role by providing key expertise in the development of indicators for monitoring and evaluation of HIV activities, including development of tools for standardizing development and dissemination of indictor data and estimates and projections describing the epidemiology of HIV/AIDS, both at the national and international level.
CDC-Global Fund Collaboration
CDC staff work with the Global Fund and Ministries of Health to provide technical support in the areas of procurement and management of drugs and equipment utilized in service provision in clinical settings and laboratory capacity-building for key personnel (management, administration, and clinical staff). In addition, CDC participates in the U.S. Government mandated parallel technical reviews of all Global Fund proposals to help inform the U.S. delegates to the Global Fund Board.
CDC-WHO Collaboration
CDC supports WHO by providing technical expertise (including CDC direct secondees to WHO-Geneva and regional programs) as well as financial support to develop programmatic and policy guidance in the areas of blood safety, injection safety, counseling and testing, male circumcision, strategic information, prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT), TB/HIV, and laboratory capacity building.
In addition, CDC facilitates sharing of WHO-endorsed best practices across countries, provides technical assistance on implementation, conducts program evaluation, and measures results to demonstrate health impact of these best practices over time.
Recent WHO-CDC Initiatives
CDC is collaborating with WHO’s Integrated Management of Adult and Adolescent Illness team on the adaptation and development of intervention and training materials for a comprehensive prevention intervention for HIV-infected individuals.
CDC sits on the STOP TB Infection Control Working Group, which develops policies and guidelines, and implements infection control practices in HIV care and TB clinical settings.
CDC has provided critical technical support in developing polices and guidelines, and tools/technical products addressing: ART treatment regimens; HIV care and support; antenatal clinic sentinel surveillance; ARV drug resistance surveillance; Laboratory methods for HIV surveillance; ART monitoring; and HIV/AIDS case reporting definitions.
CDC is working with WHO to develop guidelines on how to best implement overall quality assurance of HIV serology, CD4 counts, and viral load. This work is being done through consensus building with countries in Africa.



Labs for Life Infographic:
Get email updates
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:
Contact Us:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
1600 Clifton Rd
Atlanta, GA 30333 - 800-CDC-INFO
(800-232-4636)
TTY: (888) 232-6348
24 Hours/Every Day - Contact CDC-INFO
 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir


