Protecting the Food Supply
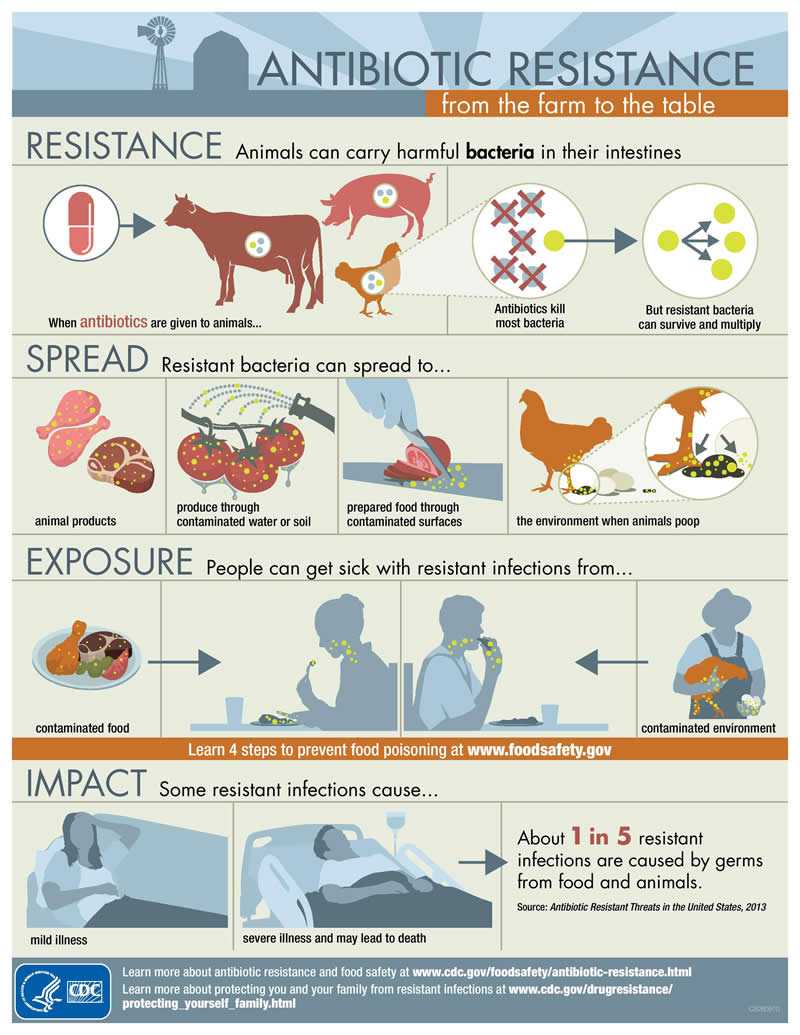
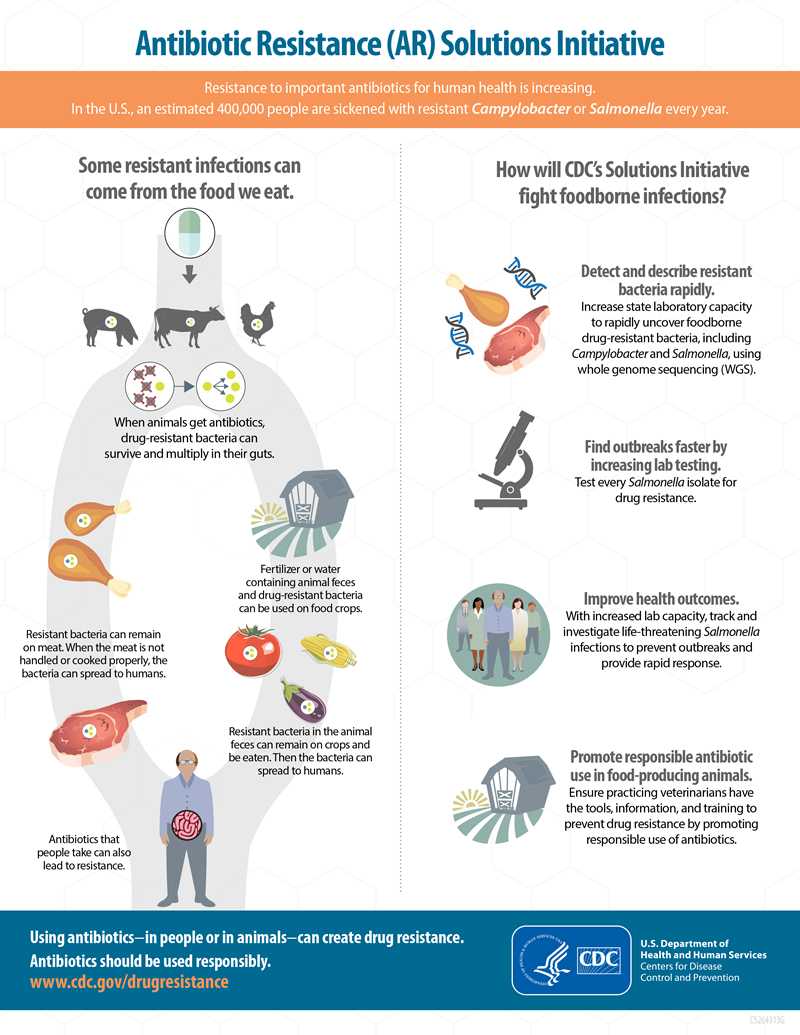
CDC estimates that more than 400,000 U.S. residents become ill with infections caused by antibiotic-resistant foodborne bacteria every year.
Antibiotic use in food animals can lead to resistant infections in humans. Studies have shown that:
- Antibiotic use in food animals allows antibiotic-resistant bacteria to grow and crowd out the bacteria that do respond to antibiotics;
- Resistant bacteria can contaminate food from the animals;
- Resistant bacteria in food can cause infections in humans; and
- These bacteria also can get into the environment through animal stool and may spread to produce that is irrigated with contaminated water.
How antibiotic resistance can spread through the food chain:
What CDC is doing to fight foodborne infections:
Learn more:
- Page last reviewed: November 15, 2016
- Page last updated: November 15, 2016
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir