Case Study: Reducing Radon in Illinois
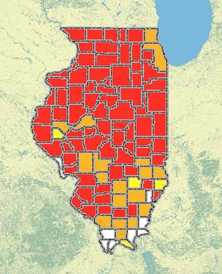
Average home radon levels by county in Illinois, 2003–2011
Adapted from the Illinois Emergency Management Agency Radon Program. Used with permission.
More than 40% of the homes tested in Illinois between 2003 and 2011 were above the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) action level of 4pCi/L (picocurie per liter); 70% of counties in the state had average radon levels above this level.
To address the radon problem, Illinois passed state laws to reduce household radon exposure. Illinois law requires—
- All new residential construction to include radon-resistant features.
- Radon professionals to be licensed.
- Radon test results to be reported to the state radon program.
- Home sellers to provide buyers with a radon notification that provides information about radon testing and recommends testing the home before purchase.
- Home sellers to provide radon test results to buyers.
- Landlords to disclose any known radon problems to tenants.
To reduce radon exposure in other building types, Illinois also recommends that schools be tested for radon every 5 years, and day care centers, homes, and group homes to be tested every 3 years.
Comprehensive Cancer Control Planning
Reducing indoor radon exposure is a goal of the Illinois Comprehensive Cancer Control Plan, 2012–2015. [PDF-861KB] The strategies to achieve this goal include increasing the number of homes and other buildings tested for radon and fixed if levels are high, developing programs to help homeowners who cannot afford to test and fix their homes, and establishing standards for radon-resistant features in new construction.
Monitoring the Effect of Radon Control Activities
The reporting requirement for licensed radon professionals gives the state radon program a more accurate picture of radon levels throughout the state. Radon monitoring also provides information needed to evaluate the effect of radon laws on the number of homes tested, and average household radon levels by county. In Illinois, the number of homes tested for radon doubled after passing the law requiring radon notification at home sales.
- Page last reviewed: April 21, 2014
- Page last updated: June 25, 2015
- Content source:
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir